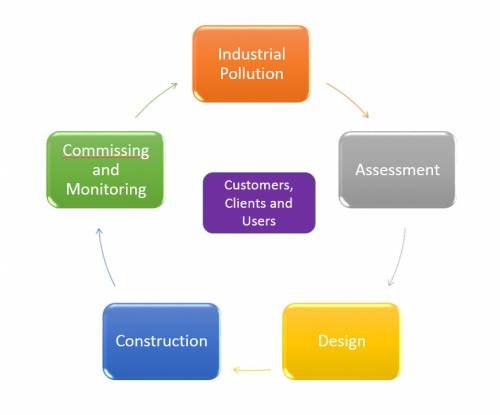
An Ecological Impact Assessment (EcIA) serves as a crucial process for pinpointing, quantifying, and evaluating the potential impacts on the ecology of a site and its surroundings due to proposed projects. This assessment, essential for both non-EIA and EIA processes, focuses on actions outside sensitive areas and those that do not exceed certain screening thresholds. It uniquely addresses the effects of a project on ecological features, emphasizing the importance of understanding the possible implications on local, regional, national, and international ecology and biodiversity.
The effectiveness of an Ecological Impact Assessment hinges on the collaboration between ecologists and other specialists to identify vital impacts on habitats, species, and ecosystems. Not only does it adhere to relevant legislation and planning policies, but it also serves as a best practice evaluation, guiding all stakeholders in acknowledging the ecological ramifications of their projects. Through this article, the key components, legislative role, and case studies of EcIA will be explored, offering insight into mitigation strategies and best practices for ecological conservation.
Understanding Ecological Impact Assessments
Ecological Impact Assessments (EcIAs) are comprehensive processes designed to evaluate the potential effects of proposed projects on various ecological parameters. These assessments play a pivotal role in ensuring that development activities are conducted responsibly, aligning with sustainability goals and legal frameworks. Below are key aspects of EcIAs:
- Process Overview:
- Initial Phase: Begins with a Preliminary Ecological Appraisal (PEA), which includes a Phase 1 habitat survey and a desk study to gather existing ecological data.
- Impact Assessment: Evaluates potential effects on protected habitats and species based on the project’s nature, using guidelines designed to assist in assessing impacts on ecosystems.
- Guidelines and Compliance:
- Integration with EIA: EcIA guidelines help integrate ecological considerations into the broader Environmental Impact Assessment (EIA) for projects that might affect ecosystems or biodiversity.
- International Frameworks: Adherence to international standards such as the Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and the International Association of Impact Assessment guidelines, which include biodiversity considerations in EIA screening and scoping phases.
- Stakeholder Engagement and Legal Considerations:
- Public Participation: Essential in the EIA process, particularly concerning indigenous communities’ rights and interests.
- Legal and Voluntary Guidelines: Includes the Akwé: Kon guidelines, which are voluntary but crucial for assessing impacts on sacred sites and lands traditionally used by indigenous and local communities.
These components underscore the importance of EcIAs in promoting environmentally sustainable development while complying with both national and international ecological and environmental standards.
Key Components of an Ecological Impact Assessment
The Ecological Impact Assessment (EcIA) process is meticulously structured to ensure thorough evaluation and mitigation of potential ecological impacts due to development projects. Here is a detailed breakdown of its key components:
EcIA Process Steps:
- Scoping and Baseline Establishment:
- Scoping: Determines the focus of the EcIA, including necessary consultations and the identification of key ecological features that might be impacted.
- Establishing the Baseline: Gathers existing ecological data to understand the pre-project conditions, aiding in the accurate assessment of potential impacts.
- Assessment and Mitigation:
- Impact Assessment: Evaluates how the project could affect identified ecological features, considering factors like impact extent, magnitude, duration, and reversibility.
- Mitigation Measures: Proposes strategies to avoid, reduce, or compensate for negative impacts, aiming for no net loss or, ideally, a net gain in biodiversity.
- Reporting and Decision Making:
- Reporting: Documents all findings, assessments, and proposed mitigation measures comprehensively.
- Decision Making: Utilizes the compiled report to guide project approvals, ensuring all ecological considerations are factored into the final decision.
Additional Considerations:
- Integration with Legal Frameworks: Ensures all assessments comply with relevant environmental laws and policies, which guide the overall EcIA process.
- Stakeholder Engagement: Involves consultations with various stakeholders, including local communities and environmental experts, to gather diverse insights and enhance the assessment’s accuracy and acceptance.
This structured approach not only facilitates responsible environmental management but also aligns project objectives with sustainability principles, ensuring long-term ecological resilience.
The Role of Legislation in Ecological Assessments
Legislation plays a pivotal role in the framework of Ecological Impact Assessments (EcIAs), ensuring that environmental considerations are integrated into both national and international development projects. The National Environmental Policy Act (NEPA) of 1969 in the U.S., for instance, mandates Environmental Impact Statements (EIS) for significant federal actions, which could affect the environment. This act is instrumental in promoting “environmental democracy,” ensuring public involvement and transparent decision-making processes.
Key Legislative Frameworks and Their Impact:
- NEPA and EIS Requirements:
- Scope: Applies to projects using federal land or funds, or those under federal agency jurisdiction.
- Outcome: Approximately 500 EIS are prepared annually, guiding responsible environmental decision-making.
- International Standards:
- Global Influence: Countries and international bodies adopt similar EIA laws, promoting sustainable development and environmental protection.
- Guidance and Compliance: The Council on Environmental Quality (CEQ) oversees NEPA regulations, addressing issues like greenhouse gases and providing categorical exclusions.
- Incorporation in National Policies:
- Malaysia: EIA procedures serve as preventive measures, integrating environmental considerations into planning to avoid adverse impacts.
- New Zealand: EcIAs support decision-making under various national legislations, emphasizing the importance of ecological evaluations in project approvals.
These legislative frameworks not only enforce compliance but also foster a culture of accountability and environmental stewardship across different jurisdictions, underscoring the importance of legal structures in ecological assessments. This ensures that development projects proceed without compromising ecological integrity, thereby supporting global sustainability objectives.
Case Studies: EcIA in Action
Ecological Impact Assessments (EcIAs) play a critical role in responsibly managing the environmental effects of development projects. They provide comprehensive data that help in making informed decisions. Here are some notable case studies that exemplify the application and outcomes of EcIAs across various regions and projects:
- Kidston Pumped Storage Hydro Project, Queensland, Australia:
- Energy Production: Generates 250 megawatts of energy.
- Cost: Estimated at $330 million.
- Environmental Impacts:
- Affects surface water quality and sedimentation.
- Impacts on macroinvertebrates and Middle Spring.
- Potential contamination during the wet season.
- BR-319 Highway, Brazil:
- Length: 870 km, connecting Manau and Porto Velho.
- Environmental Consequences:
- Potential deforestation of up to 39 million hectares.
- CO2 emissions projected to exceed 47 billion tons by 2050.
- Opens untouched forest areas to development.
- Conservation Efforts:
- Cape Floristic Region, South Africa:
- Achieved conservation targets, establishing a network of protected areas.
- Conchalí Lagoon, Chile:
- Managed by Los Pelambres copper mining as a Nature Sanctuary.
- Supports diverse biological flora and fauna.
These cases demonstrate the varying scale and nature of projects and the critical role of EcIAs in mitigating environmental impacts while facilitating sustainable development.
Mitigation Strategies and Best Practices
Mitigation strategies in ecological impact assessments (EcIAs) are crucial for minimizing adverse effects on the environment. These strategies are systematically categorized under the mitigation hierarchy, which includes avoidance, minimization, rehabilitation/restoration, and offset. Here’s an overview of best practices in implementing these strategies:
Mitigation Hierarchy and Best Practices
- Avoidance:
- Prioritize the preservation of habitats critical to ecological processes as they support ecosystem services.
- Implement careful planning to prevent impacts to sensitive ecological areas.
- Minimization:
- Employ noise reduction technologies and refine processes to mitigate hazardous spills.
- Enhance project delivery processes to minimize transportation-related impacts on ecosystems.
- Rehabilitation/Restoration:
- Restore or compensate for lost habitats where possible.
- Maintain or restore the natural pattern and connectivity of habitat patches to support biodiversity.
- Offset:
- Implement supporting conservation actions that provide positive effects on biodiversity, albeit difficult to quantify.
- Develop and apply advanced mitigation measures such as biogenic-based sequestration techniques and geoengineering to manage radiative forcing.
Monitoring and Compliance
- Effectiveness Monitoring: Regularly monitor the effectiveness of mitigation measures and prepare to implement alternative strategies if the initial measures are insufficient.
- Compliance and Enforcement: Conduct environmental auditing at the end of the project to evaluate the accuracy of the EIA and ensure compliance with environmental laws.
Advanced Mitigation Technologies
- Carbon Management: Utilize negative emissions technologies to capture and sequester atmospheric carbon, reducing overall CO2 levels.
- Innovative Approaches: Explore geoengineering techniques to stabilize or reduce global temperatures, complementing traditional mitigation strategies.
By integrating these mitigation strategies and monitoring their effectiveness, stakeholders can significantly reduce the ecological impacts of development projects, ensuring sustainable and responsible environmental management.
Conclusion
Throughout this article, we have delved into the intricacies of Ecological Impact Assessments (EcIAs), highlighting their critical role in maintaining ecological integrity in the face of development. From outlining the fundamental processes and guidelines for conducting EcIAs to examining case studies that demonstrate their practical applications, we have emphasized the importance of thorough assessment and mitigation strategies for safeguarding biodiversity. The discussion has underscored how these assessments not only comply with legal frameworks but also foster a culture of environmental stewardship, ensuring that projects advance without detrimental effects on our natural surroundings.
As we reflect on the significance of EcIAs within global sustainable development practices, it becomes clear that the integration of ecological considerations in project planning is not just beneficial but imperative. The implementation of effective mitigation hierarchies, coupled with continuous monitoring and adaptation of strategies, presents a path toward minimizing environmental impacts while promoting conservation. By adhering to the principles and best practices outlined in this exploration, stakeholders across various sectors can contribute to a more sustainable and ecologically responsible future. This commitment to ecological assessment and management underscores our collective responsibility towards preserving the planet for future generations.