Vectors have several applications both in physics and engineering. Vectors as a concept started close to two centuries back and were used in representing physical quantities like velocity, displacement, and acceleration. With the advent of electromagnetic field induction, the use of vectors started in the latter part of the 19th century.
With the solved examples for types of vectors, you can understand the topic much better.
Explain vectors
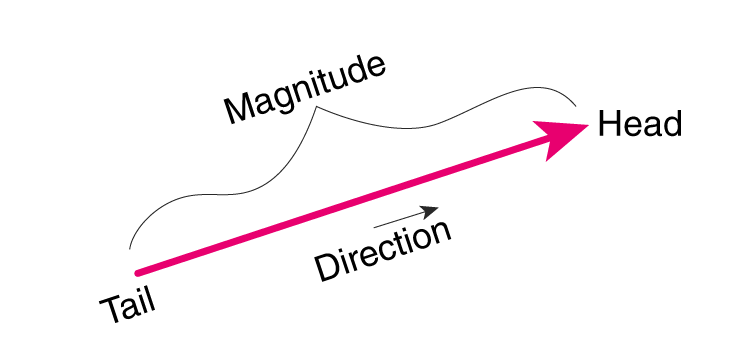
Vector means carrier. It is a Latin word. Vectors define point A to point B. The length between the two points is the vector magnitude—the displacement direction of point A to point B in the direction of the vector AB. Vectors are used a lot in physics subjects.
Displacement, velocity, and acceleration are vector quantities that have both a magnitude and a direction.
The standard way to represent a vector is by A=a^i b^j c^k where a, b, and c, all have numeric values and ^i,^j,^k are the unit vectors represented along the x, y, and z-axis, respectively.
The different kinds of vectors
The vector property determines the naming of the vector. These different vectors help in carrying our arithmetic operations and calculations.
- Zero Vectors: As the name implies, a zero vector has a 0 magnitude. It also does not have any direction. This is called the vector’s additive identity.
- Unit Vectors: Unit vectors are those that have a magnitude that equals 1. This is the multiplicative identity of the vector. The length of this vector is 1, and it is used to demonstrate the direction of the vector.
- Position Vectors: Position vectors are used to find out the direction and the position of the movement of the vector in any three-dimensional space. It is possible to change the position vector’s direction and magnitude in relation to any other body. This vector is also referred to as a location vector.
- Equal Vectors: Two or more vectors are equal when their components that are creeping in are also equal. These have both the same direction and magnitude. These could have different initial and terminal points, but the length and direction are absolutely the same.
- Negative Vectors: A negative vector is another vector that has the same magnitude but opposite direction. So if you assume that there is a vector A and a vector B, they will have the same magnitude but different directions. In this case, you say that vector A is the negative of vector B
- Parallel Vectors: If two or more vectors have a similar direction but not the same magnitude, these are parallel vectors. If you calculate the angle between two parallel vectors, then it is zero. If the angle of direction between two vectors is 180 degrees, then these are antiparallel vectors. These are vectors that have an opposite direction.
- Orthogonal Vectors: If there are two or more vectors in space and the angle between them is 90 degrees, these are orthogonal. The dot product of these two vectors is always 0.
- Co-initial Vectors: The vectors that start from the same starting paint are called co-initial vectors.
Different Vectors and their properties
You can do different mathematical operations on the vectors. These include simple math like addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Here are the different vector properties that you should be aware of.
- Vector addition is associative and commutative.
- The dot product of two vectors is a scalar quantity and will lie in the two vectors place.
- The cross product of any two vectors is also a vector, and it lies perpendicular to the plane that consists of these two vectors.
Vector application
Here are some crucial vector applications in real life.
- You can use vectors to understand the direction of the force that you apply to move any object.
- Vector is used to understand the force of gravity and how it is applied to objects moving in the vertical direction.
- Vectors let you obtain the body’s motion that is confined to a plane.
- Vectors let you define the force that is applied to three dimensions on a body at the simultaneously same time.
- Vectors find use in engineering where it helps to check if the force is stronger than what the structure will be able to bear. If that is the case, then the force needs to be reduced else the structure will collapse.
- Vectors are used in several oscillators.
- Vectors find use in quantum mechanics.
- Vectors are used to find the velocity of the flow of liquid in a pipe. This can be found using a vector field.
- Vectors can be seen in everyday life in general activities.
- Vectors are used in vibration and sound propagation.
Solved examples
Here are some solved examples for you to better understand the types of vectors:
Example 1: Which vectors have the same direction but do not have the same magnitude?
The vectors that have the same direction but do not have the same magnitude are called parallel vectors.
Example 2: If two vectors have an angle that differs by 180 degrees, what are they called?
Vectors that have an angle of 180 degrees are called antiparallel vectors.
Example 3: What are co-initial vectors?
Vectors that have the same start point are known as co-initial vectors.
Conclusion
A vector is a geometrical entity with both a direction and a magnitude. A line can represent the vector, and it has an arrow that points towards the direction. The length of the vector is a representation of its magnitude. Vectors are thus represented with the help of arrows that have both an initial and a terminal point. Vectors are also associated with art work as well. You probably heard about vector images which are used in various things including logos, designs, prints etc. These are vector designs which you can download from various sources from the internet for your online magazines, business logos etc. Get Vectors is one of the best places where you can download the free and premium vectors online.
FAQs
Q1. What are vectors?
Vector is a geometrical or physical quantity that has both direction and magnitude.
Q2. What are some examples of vectors?
Vector quantities are those physical quantities that are specified by their direction and magnitude. These include velocity, displacement, torque, etc.
Q3. How can vectors be used in our day-to-day life?
Vectors are used to represent the aircraft’s velocity, where you need to know the speed and direction of the aircraft. Electromagnetic induction also uses vectors which is the interplay of magnetic and electric forces.